
Copyright gives protection to the owner of the rights to an original work. The owner will often be the creator, although this is not always the case.This means that individuals who want to reproduce the original work of others may need to seek permission to do so.
although this is not always the case.This means that individuals who want to reproduce the original work of others may need to seek permission to do so.
Copyright...

Copyright law applies to a broad range of intellectual property, including:
The minimum punishment for infringement of copyright for a term which shall not be less than six months but which may extend to three years and with fine which shall not be less than fifty thousand rupees but which may extend to two lakh rupees.
FOR ALL INFORMATION ON COPYRIGHT IN INDIA- PLEASE ACCESS THIS GOVERNMENT OF INDIA SITE ON COPYRIGHT AND THE COPYRIGHT ACT, 1957 (14 OF 1957)

Plagiarism is best defined as the unacknowledged use of another person’s work. It is an ethical issue involving a claim of credit for work that the claimant did not create. One can plagiarize someone else’s work regardless of the copyright status of that work. For example, it is nonetheless plagiarism to copy from a book or article that is too old to still be under copyright. It is also plagiarism to use data taken from an unacknowledged source, even though factual material like data may not be protected by copyright. Plagiarism, however, is easily cured – proper citation to the original source of the material.
Copyright infringement, on the other hand, is the unauthorized use of another’s work. This is a  legal issue that depends on whether or not the work is protected by copyright in the first place, as well as on specifics like how much is used and the purpose of the use. If one copies too much of a protected work, or copies for an unauthorized purpose, simply acknowledging the original source will not solve the problem. Only by seeking prior permission from the copyright holder does one avoid the risk of an infringement charge.
legal issue that depends on whether or not the work is protected by copyright in the first place, as well as on specifics like how much is used and the purpose of the use. If one copies too much of a protected work, or copies for an unauthorized purpose, simply acknowledging the original source will not solve the problem. Only by seeking prior permission from the copyright holder does one avoid the risk of an infringement charge.

Copyright does not protect ideas, only the specific expression of an idea. For example, a court decided that Dan Brown did not infringe the copyright of an earlier book when he wrote The Da Vinci Code because all he borrowed from the earlier work were the basic ideas, not the specifics of plot or dialogue. Since copyright is intended to encourage creative production, using someone else’s ideas to craft a new and original work upholds the purpose of copyright, it does not violate it. Only if one copies another’s expression without permission is copyright potentially infringed.
To avoid plagiarism, on the other hand, one must acknowledge the source even of ideas that are borrowed from someone else, regardless of whether the expression of those ideas is borrowed with them. Thus a paraphrase requires citation, even though it seldom raises any copyright problem.

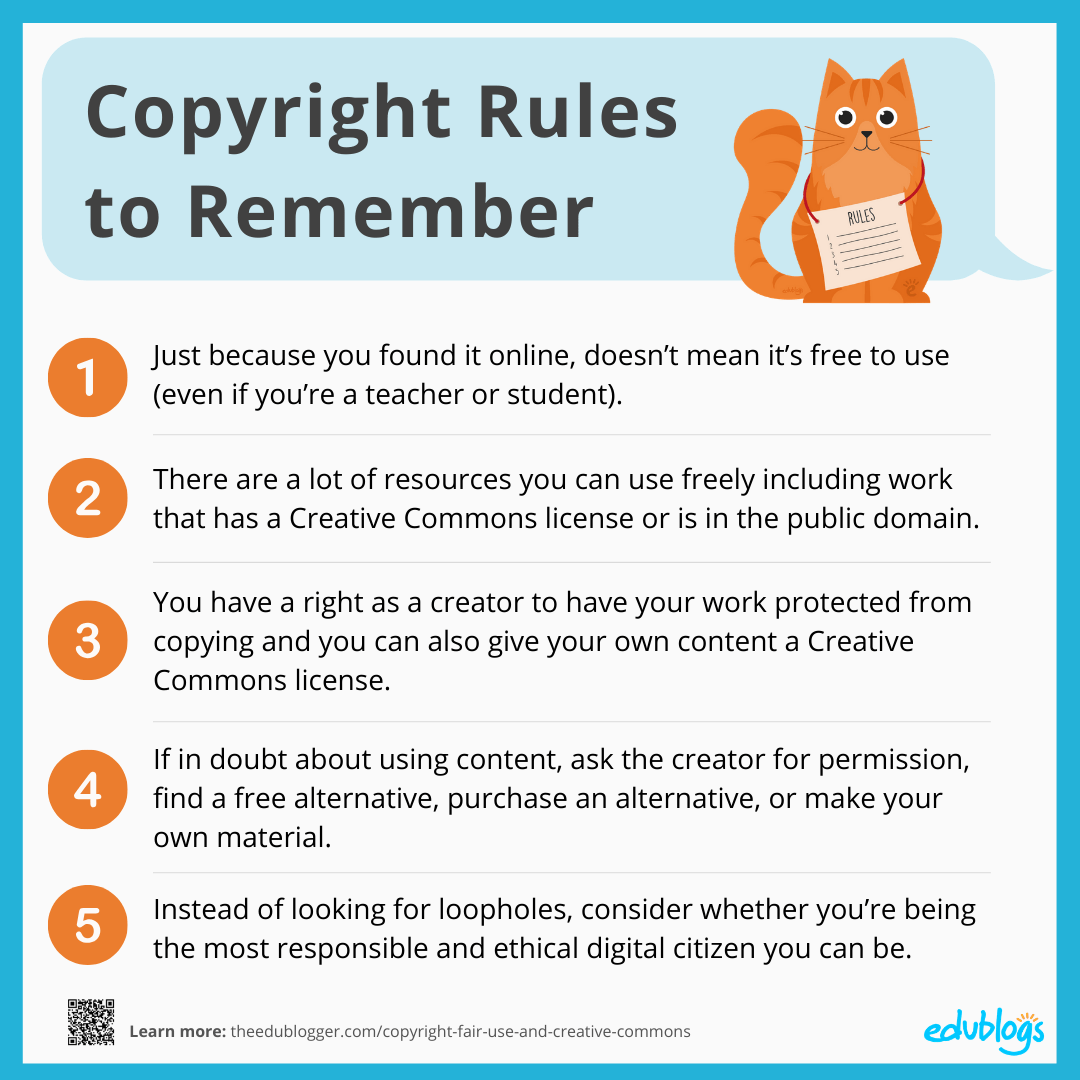
Possibly, but not necessarily. Fair Use allows limited use of copyrighted works without requiring permission from the copyright holder for a number of educational purposes -- commentary, criticism, research, teaching, or scholarship. However, it is important to remember that an educational purpose alone does not mean that your use will be protected as Fair Use. Copyright law sets forth a number of fact-specific criteria that must be evaluated to determine whether a use is "Fair."
If you don't buy your own copy of the textbook, you are violating copyright law as well as stealing from the textbook publisher.
Generally, merely providing links to materials on the web does not require the permission of the copyright holder. It is a good rule of thumb to use linking to provide access to copyrighted materials whenever possible, rather than posting PDFs or otherwise reproducing web materials.
There are many reasons a work might be in the public domain. A few common reasons are:



Common symbols for public domain works. Also look for works labeled as "no known copyright restrictions"