
False Information v Fake News
There are a number of things to watch out for when evaluating content online.
Click away from the story to investigate the site, its mission and its contact info.
If the piece has an author, do a search to evaluate credibility. Is this person a recognized expert?
Reposting older news does not mean its relevant to current events.
Consider if your own beliefs could affect your judgment on this topic.
Headlines can be outrageous in an effort to get clicks. What's the whole story?
Click links or search for any source information provided. Does the info support the story?
The story might be satire. Research the site to be sure.
Ask a librarian, your instructor or a known expert or consult a fact-checking site.
Adapted from a graphic produced by the International Federation of Library Associations . For more information:
Deepfakes are fake videos created using digital software, machine learning and face swapping. Deepfakes are computer-created artificial videos in which images are combined to create new footage that depicts events, statements or action that never actually happened. The results can be quite convincing. Deep fakes differ from other forms of false information by being very difficult to identify as false.
The basic concept behind the technology is facial recognition, users of Snapchat will be familiar with the face swap or filters functions which apply transformations or augment your facial features. Deep Fakes are similar but much more realistic. Fake videos can be created using a machine learning technique called a “generative adversarial network” or GAN. For example a GAN can look at thousands of photos of Beyonce and produce a new image that approximates those photos without being an exact copy of any one of the photos. GAN can be used to generate new audio from existing audio, or new text from existing text – it is a multi-use technology. The technology used to create Deep Fakes is programmed to map faces according to “landmark” points. These are features like the corners of your eyes and mouth, your nostrils, and the contour of your jawline.
There are differing opinions when it comes to identifying types of false information. However, when it comes to evaluating content online there are various types of false or misleading news we need to be aware of. These include:
These are stories that are deliberately fabricated to gain more website visitors and increase advertising revenue for websites. Clickbait stories use sensationalist headlines to grab attention and drive click-throughs to the publisher website, normally at the expense of truth or accuracy.

Stories that are created to deliberately mislead audiences, promote a biased point of view or particular political cause or agenda.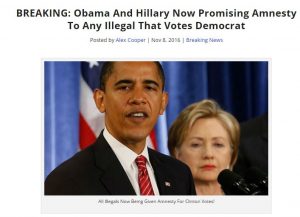
Sometimes reporters or journalists may publish a story with unreliable information or without checking all of the facts which can mislead audiences. For example, during the U.S. elections, fashion retailer Urban Outfitters published an Election Day Guide, the guide contained incorrect information telling voters that they needed a ‘voter registration card’. This is not required by any state in the U.S. for voting.
Stories that are not completely false can be distorted using misleading or sensationalist headlines. These types of news can spread quickly on social media sites where only headlines and small snippets of the full article are displayed on audience newsfeeds.
Many people are drawn to news or stories that confirm their own beliefs or biases and fake news can prey on these biases. Social media news feeds tend to display news and articles that they think we will like based on our personalised searches.
Satire
Satire news or comedy news often begins with an aspect of truth then purposefully twists it to comment on society. Satire news has the potential to be spread as though it is real news by those who do not understand its humorous nature. An example of a well-known satire website is The Onion.
SOURCE:
Explained: What is Fake news? | Social Media and Filter Bubbles. (2020, March 2). Webwise.ie. https://www.webwise.ie/teachers/what-is-fake-news/